The ILA strike that commenced on Oct. 1 ended abruptly after pressure from industry leaders and the Biden administration pushed the ILA and USMX to iron out a tentative deal, with the labor union walking away with a 62% compounded wage increase over the six-year contract. In other news, transportation jobs continued to decline since their peak in March 2024, prompting economists’ concerns about the instability of transportation and warehousing, with signs that hiring remains weak despite broader economic resilience.
Continue reading as we explore that and other news and trends shaping the freight world.
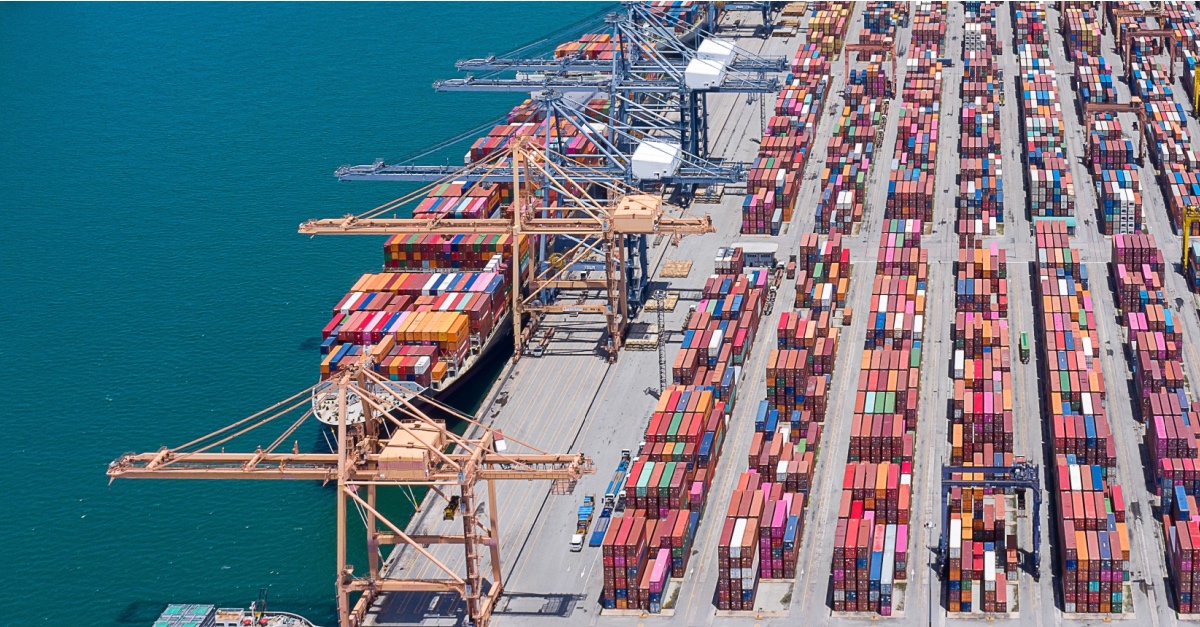
US East and Gulf Coast Ports Reopen as Dockworkers End Strike
US East and Gulf Coast ports have reopened after a three-day strike by dockworkers, which ended with a 62% wage increase for union members over the next six years. The strike shut down operations in ports from Maine to Texas and threatened to disrupt vital supply chains just weeks before the presidential election. The new wage offer, spurred by pressure from the White House, is higher than the previously proposed 50% raise but falls short of the 77% demanded by the union.
Although some ports will take time to return to full operations, the shipping backlog is being cleared. The deal marks a victory for Harold Daggett, the International Longshoremen’s Association (ILA) leader, and will result in higher costs for shipping companies like Maersk and COSCO. President Biden has praised the agreement as a win for collective bargaining while employers and dockworkers continue to negotiate other issues, such as port automation.
Decline in Transportation and Warehousing Jobs Signals Challenges in the Logistics Sector
The US Bureau of Labor Statistics’ October jobs report shows a continued decline in truck transportation and warehousing employment that has persisted since peak employment numbers in March 2024. Truck transportation jobs dropped by 700 in September and have shed 12,800 jobs since March, influenced partly by the Yellow Corporation bankruptcy, which caused a loss of 21,000 jobs in the less-than-truckload sector.
The warehousing and storage sector saw a significant decline, losing 11,000 jobs in September, following a similar drop in August. The drop also marks a reversal after gains earlier in 2024, with warehousing jobs now just 4,700 above the March low. Warehousing jobs peaked in May 2022 during the pandemic boom but have since experienced a steep decline.
US-Mexico Logistics Expansion Faces Challenges Amid Growing Cross-Border Trade
Logistics providers across the US are enhancing operations to accommodate the rising trade flows between the US and Mexico amid significant challenges that could derail operations. The recent ILA strike highlighted Mexico as an alternative route for US-bound cargo, with logistics companies like Cargado and XPO expanding cross-border services. XPO’s Mexico+ service now covers 99% of Mexico’s postal codes.
However, despite these expansions, infrastructure and security issues are significant obstacles. Mexican ports like Altamira and Veracruz are limited by capacity, and road and rail infrastructure remain insufficient. Additionally, Mexico’s customs regulations are strict, and the imbalance in trade flows between the US and Mexico complicates logistics. The ratio of trucks crossing north-south is 5:1, leading to pricing challenges as Mexican truckers account for empty return trips.
Crime on Mexican highways and railways is another concern, driving up transportation costs by 27%.
LA-LB Ports Achieve Major Emissions Reductions but Face Future Challenges
Los Angeles and Long Beach ports made significant strides in reducing emissions in 2023, largely due to decreased vessel arrivals and cleaner cargo-handling practices. The ports have been able to cut diesel particulate matter (DPM) by 91%, nitrogen oxides (NOx) by 72%, sulfur oxides (SOx) by 98%, and greenhouse gases (GHG) by 20%.
These improvements follow the Clean Air Action Plan (CAAP) adopted in 2006, which aims to transition to zero-emission marine terminals by 2030 and drayage trucks by 2035. Despite these advancements, the path forward presents tougher challenges. Regulatory mandates from federal, state, and regional bodies impose additional costs and pressures on port operations. Stakeholders expressed concerns that stringent independent source rules (ISRs) could restrict port cargo volume.
Surge in Cargo Thefts Spurs Debate on Rail Security Measures
Cargo theft continues to plague US railways, with incidents jumping 49% in the first half of 2024. Criminals have enjoyed so much success that it has sparked debates over whether heavy-duty locks and security devices help or hinder theft prevention. Supporters argue that these locks make containers harder targets, but critics suggest they may attract more attention or create logistical complexities for rail operators.
Additionally, concerns about insider threats are growing as individuals with access to sensitive data use it for theft. While industry efforts to improve security include enhanced locks and strategic placement of containers, some experts suggest limiting access to specific brand information could further reduce risks. Most experts agree that navigating these challenges requires balancing security measures and operational efficiency.
Transportation Never Sleeps With COGISTICS Transportation
We’re not just the average logistics provider in the market; we transform logistics challenges from air, land, and ocean freight operations into strategic advantages around the clock and worldwide. Whether consolidating shipments or pushing expedited freight, you can trust COGISTICS Transportation’s 3PL solution to have your back. Leveraging over 30 years of expertise, we provide innovative, technology-driven logistics solutions by land, air, and sea — around the clock, around the world. Connect with us today to see the difference.